March 01, 2024 Industry news
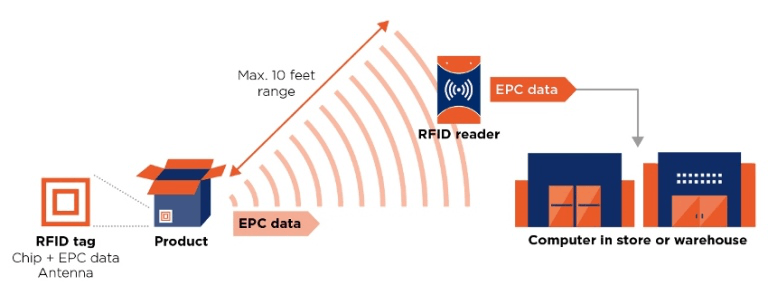
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify and track objects. It works by encoding unique identifiers into ‘tags’; tiny electronic devices or microchips that can be attached to any object or item that needs tracking.
These tags can be passive, semi-passive, or active. Passive tags do not have their power source and are activated by an RFID reader's electromagnetic field. Semi-passive tags have their own power source but still rely on the reader's field to communicate. Active tags have their own power source and can transmit signals independently.
A reader is the device that emits the radio waves that communicate with RFID tags. It sends out electromagnetic waves using an antenna and, when a tag enters the reader's field, it receives power from these electromagnetic waves and sends back its unique identifier along with any other data it may contain.
RFID in construction
RFID tags can be used to capture unique identifiers, such as GS1 Global Trade Item Numbers (GTINs) and other Electronic Product Codes (EPCs), at extremely high rates and at distances well in excess of ten metres, without line-of-sight contact.
They can also withstand extremely harsh environments making them a powerful tool for stakeholders across the construction industry.
GS1 standards act as a complementary layer to RFID technology, providing a standardised language for the data encoded on each tag for full interoperability.
The use of GS1 powered RFID tags in construction continues to gain momentum and new digital initiatives are emerging all over the world as industry and regulators seek to create safer, more efficient and more sustainable supply chains.
The benefits of RFID
Adopting RFID enables the movement and location of materials and assets to be tracked with high accuracy at high speed. This helps to avoid overstocking, understocking and loss, optimises deliveries by ensuring materials arrive only when needed, and reduces storage needs and waste.

Using RFID to monitor equipment usage over time allows stakeholders to predict maintenance needs and avoid costly breakdowns. It can identify underused resources to avoid waste and locate missing or hard to find equipment, reducing staff hours and replacement costs.
Increased safety is a key benefit. By facilitating highly targeted quality control checks, RFID can prevent the use of faulty, non-compliant or counterfeit products. In emergencies, it enables far more efficient recalls and the detection of defective materials. It can even be used to identify and track workers in hazardous areas, blocking access to non-authorised personnel or enabling faster responses from emergency responders.
RFID and BIM
RFID technology can also be integrated with Building Information Modelling (BIM). BIM is essentially a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure.
It allows multiple stakeholders such as architects, engineers, contractors and facility managers to work collaboratively on a single shared digital platform. This helps to reduce errors, improve coordination, and enhance overall project management.
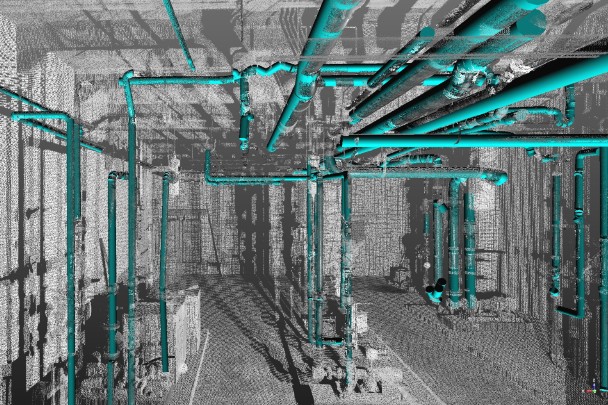

BIM is much more than a 3D design. It integrates various types of data to create a detailed "digital twin" of a project. This process helps all those involved in the different stages of a building’s lifecycle manage and exchange data, all the way from initial design through to demolition.
RFID can and increasingly does play a crucial role in the effectiveness of these digital twins.
The real-time tracking of works, assets and materials it powers is a crucial element of the data-driven decision making that BIM is known for.